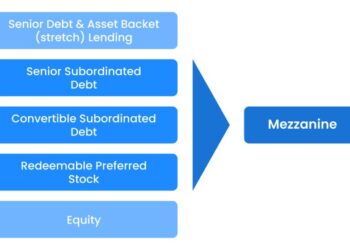
Delving into the realm of loan security in finance, this guide aims to shed light on the essential concepts for beginners. From understanding the significance of loan security to exploring different types of securities, this topic offers a foundational understanding crucial for navigating the world of finance.
In the following paragraphs, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of loan security, providing insights and examples to enhance your comprehension.
Introduction to Loan Security

Loan security in finance refers to the assets or collateral that a borrower pledges to a lender to secure a loan. This collateral acts as a form of protection for the lender in case the borrower defaults on the loan.
Loan security is an essential aspect of lending practices as it helps mitigate the risk for the lender and provides assurance that the loan will be repaid.
Importance of Loan Security
Loan security plays a crucial role in lending practices by reducing the risk for lenders. By providing collateral, borrowers demonstrate their commitment to repaying the loan, making them more creditworthy. In the event of default, the lender can seize and sell the collateral to recover the amount owed.
This security allows lenders to offer lower interest rates and more favorable terms to borrowers.
- Examples of common types of loan securities include:
Real Estate
Real estate, such as a home or commercial property, can be used as collateral for a loan. In the event of default, the lender can foreclose on the property to recover the outstanding debt.
Automobiles
Vehicle loans often use the car itself as collateral. If the borrower fails to make payments, the lender can repossess the vehicle to cover the remaining balance.
Investments
Stocks, bonds, or other investment assets can also be pledged as collateral for a loan. These securities provide a source of repayment for the lender if the borrower defaults.
Types of Loan Securities

When it comes to loans, there are two main types of loan securities: secured loans and unsecured loans. Let's delve into the differences between the two and how collateral plays a crucial role in securing a loan.
Secured Loans vs. Unsecured Loans
In secured loans, borrowers pledge collateral as a form of security to the lender. This collateral acts as a guarantee that the loan will be repaid. On the other hand, unsecured loans do not require any collateral and are approved based on the borrower's creditworthiness.
- Secured loans offer lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans due to the reduced risk for the lender.
- Unsecured loans are typically harder to qualify for since they rely solely on the borrower's credit history and income.
Collateral in Securing a Loan
Collateral refers to assets that borrowers pledge to lenders to secure a loan. These assets serve as a form of security in case the borrower defaults on the loan. Common examples of collateral include real estate, vehicles, savings accounts, or valuable possessions.
- By providing collateral, borrowers can access larger loan amounts and better terms.
- If a borrower fails to repay a secured loan, the lender has the right to seize and sell the collateral to recoup the outstanding debt.
Examples of Assets as Collateral
Various assets can be used as collateral to secure a loan, such as:
- Real Estate:Properties like homes, land, or commercial buildings.
- Vehicle:Cars, motorcycles, boats, or other valuable transportation assets.
- Investments:Stocks, bonds, or other investment portfolios.
Understanding Collateral
Collateral plays a crucial role in securing a loan by providing a form of security for the lender in case the borrower defaults on the loan. It acts as a guarantee that the lender can recoup their funds through the liquidation of the collateral if necessary
Role of Collateral in Securing a Loan
Collateral serves as a form of protection for lenders, reducing the risk associated with lending money. By pledging an asset as collateral, the borrower demonstrates their commitment to repaying the loan. In the event of default, the lender can seize and sell the collateral to recover the outstanding debt.
Impact of Collateral Value on Loan Terms
The value of the collateral directly impacts loan terms such as interest rates, loan amounts, and repayment periods. Higher-value collateral typically leads to more favorable loan terms, as it provides greater assurance to the lender in case of default. On the other hand, lower-value collateral may result in higher interest rates or stricter repayment terms.
Evaluating Collateral for Loan Security
Lenders carefully assess the value, liquidity, and marketability of the collateral when evaluating loan security. The value of the collateral should be sufficient to cover the loan amount in case of default. Factors such as market fluctuations, depreciation, and condition of the collateral are considered during the evaluation process to ensure adequate security for the loan.
Loan Security and Risk Management
Loan security plays a crucial role in risk management for lenders, helping to mitigate potential losses in case of borrower default. By providing an asset as collateral, the lender has a form of security that can be used to recover the loan amount in case the borrower fails to repay.
Relationship between Loan Security and Interest Rates
- Loan security influences interest rates: Lenders often offer lower interest rates on loans secured by collateral since the risk of default is lower.
- Higher security may lead to lower interest rates: The greater the value of the collateral provided, the lower the interest rates offered by lenders.
- Unsecured loans have higher interest rates: Loans without collateral pose a higher risk for lenders, resulting in higher interest rates charged to compensate for the increased risk.
Impact of Loan Security on Borrower's Risk Profile
- Reduced risk for borrowers with collateral: Providing security can improve the borrower's risk profile, making it easier to access loans and potentially at lower interest rates.
- Default consequences: In the event of default, borrowers risk losing the collateral they pledged, which could have long-term financial implications.
- Improved creditworthiness: Successfully repaying a secured loan can enhance the borrower's credit history and overall creditworthiness, opening up more financial opportunities in the future.
Legal Aspects of Loan Security
When it comes to loan security, understanding the legal implications is crucial for both borrowers and lenders. The legal framework surrounding collateral and loan security agreements dictates the rights and responsibilities of each party involved. Additionally, the process of enforcing loan security in the event of default is a critical aspect that needs to be clearly understood by all parties.
Implications of Using Collateral for Loan Security
Collateral serves as a form of security for lenders in case borrowers default on their loans. It provides a legal guarantee that the lender can recover their funds by seizing and selling the collateral if necessary. However, borrowers need to be aware that failure to repay the loan can result in the loss of the collateral, which could be a valuable asset such as a property or vehicle.
Rights and Responsibilities of Borrowers and Lenders
In a loan security agreement, borrowers have the responsibility to provide the agreed-upon collateral and make timely repayments as per the terms Artikeld in the contract. On the other hand, lenders have the right to enforce the collateral in the event of default, following the legal procedures set forth in the agreement.
It is essential for both parties to fully understand their rights and obligations to avoid disputes or legal issues.
Enforcing Loan Security in the Event of Default
When a borrower defaults on a loan, lenders have the legal right to enforce the loan security by seizing and selling the collateral to recover the outstanding debt. This process typically involves following specific legal procedures and may require court intervention in some cases.
It is important for lenders to adhere to the legal requirements when enforcing loan security to ensure a fair and lawful resolution to the default situation.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, grasping the nuances of loan security is paramount for anyone venturing into the financial landscape. By comprehending the role of collateral, risk management implications, and legal aspects, individuals can make informed decisions when it comes to borrowing and lending.
FAQ Overview
What is the importance of loan security?
Loan security provides a safety net for lenders by ensuring that they have a way to recover their funds if a borrower defaults on the loan.
What are examples of common types of loan securities?
Common examples include real estate, vehicles, savings accounts, and valuable possessions that can be used as collateral.
How does collateral impact loan terms?
The value and type of collateral can affect the interest rate, loan amount, and overall terms of the loan.
What is the process of enforcing loan security in case of default?
In the event of default, lenders can take legal action to seize the collateral used to secure the loan.